Fragmentation Utility
In the Fragmentation utility, you can use the Swebrec function to analyse fragmentation.
Fragmentation by blasting refers to the process of using explosives to break rock into small pieces that can be efficiently excavated. Optimising blasting is an important preparatory step for extraction, waste management and reduction of further processing.
The Swebrec function is a fragment size distribution function that links rock fragmentation by blasting and crushing. The function is used to help predict fragment size as a result of blasting.
The Swebrec function is combined with the Kuz–Ram model, the Crush Zone Model and Two-Component Model of rock blasting, the JKMRC approach to describing crusher circuits, and the original natural breakage characteristic concept of material-specific size distribution curves in comminution.
The Swebrec function can entirely replace the Rosin–Rammler function in the extended Kuz–Ram model. This modified extended model is called the KCO model.
In DataBlast Ignite, the Swebrec function is used to model the distribution of particle sizes. When plotted on a chart, the proportion of the rocks of each size typically forms an 'S' curve. The chart illustrates what percentage of the blasted material is expected to be in fragments smaller than a certain size. The fragment sizes are in a logarithmic scale along the X-axis of the chart.
Multiple models can be displayed on the same chart for comparison. The following screenshot displays the effect of different burden and spacing on fragmentation.
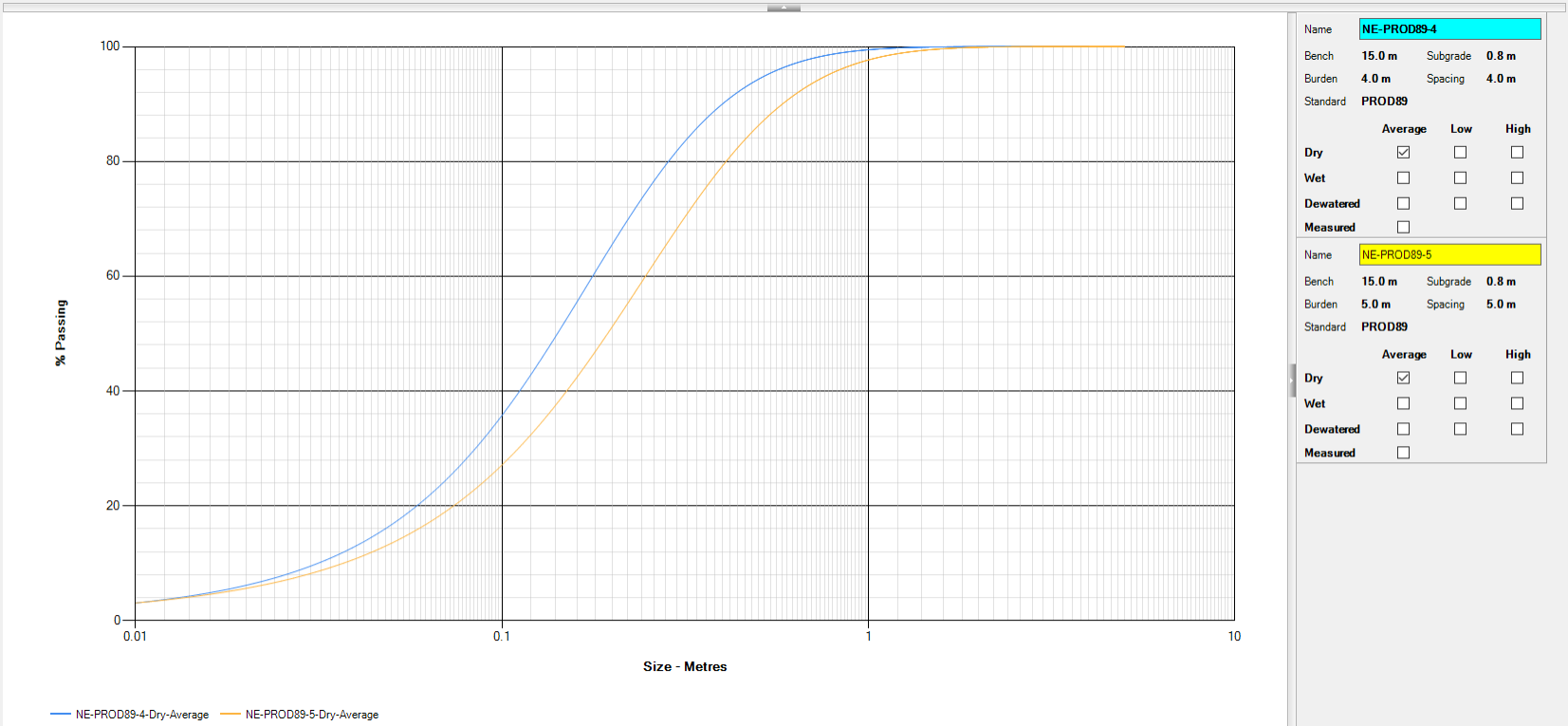
Each model is specific to a rock type. DataBlast Ignite includes default variables (for example, for density and strength) for many different rock types. However, to improve the accuracy of the model, fragmentation must be calibrated on a site level; for example, by using photo analysis tools such as WipFrag™.
Note: For DataBlast Ignite 2.8, the Fragmentation utility is only compatible with the metric measurement type.