Filtering Property
Filtering is used to select and display the object associated to values in a given range or associated to a set of categories in a catalog for a given variable. Tick Activate to activate a filter, click on the variable selector to define a first criterion on filtering.
Note: The variable selector is initialized on the variable used to display the item at first, if any.
-
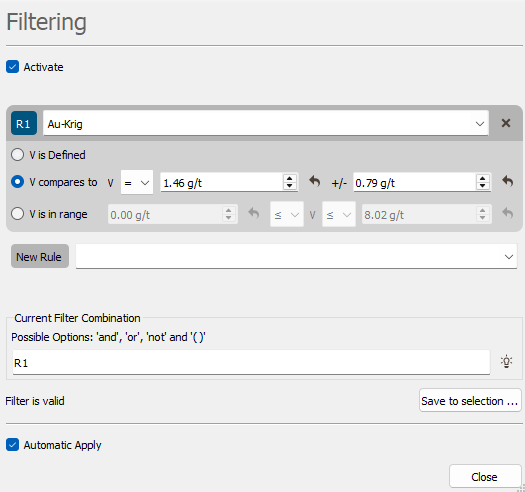
If the selected variable is a numerical variable, three criteria may be used to apply the filtering:
- V is Defined. Only the objects for which the value of the selected variable is defined are displayed.
- V compares to. The variable is compared to a value (<, ≤, >, ≥, =, ≠) with a certain tolerance. Only the objects for which the value of the selected variable respects the equality are displayed.
- V is in range. The variable is compared to an interval (exclusive or inclusive). Only the objects for which the value of the selected variable fits the interval are displayed.
-
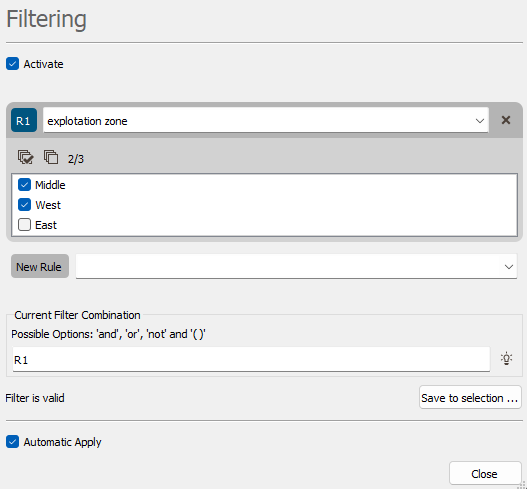
If the selected variable is a categorical variable, tick the categories that you want to keep (the unticked categories are filtered).
-
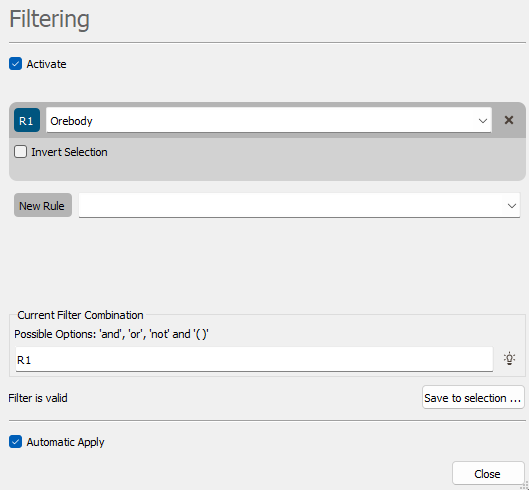
If the selected variable is a selection variable, the samples activated by the selection (i.e. equal to 1) are kept by default. Tick the Invert Selection toggle to select the samples masked off by the selection (i.e. equal to 0).
-
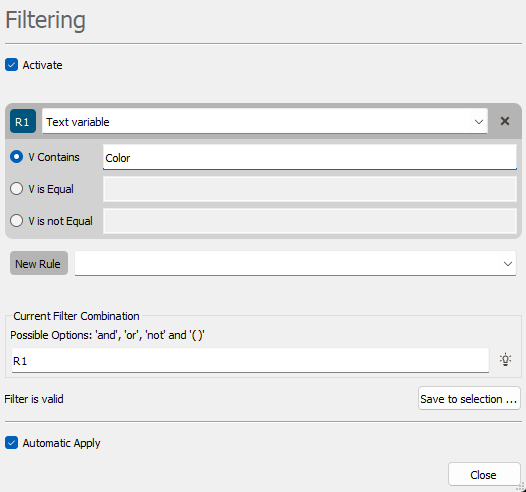
If the selected variable is a text variable (i.e. a string of characters), three criteria may be used to apply the filtering:
- V Contains. Only the objects for which the selected variable contains the given string of characters are displayed.
- V is Equal. Only the objects for which the selected variable is identical to the given string of characters are displayed. This criterion is sensitive to capital/small letters.
- V not Equal. Only the objects for which the selected variable is different from the given string of characters are displayed.
-
Current Filter Combination: You can add / remove several different criteria achieved on different variables selecting a variable next to New Rule. By default the criteria are combined by a logical "and" operator but you can modified the rules. Each rule is numbered from 1 to N (the rule number is recalled in its name). The authorized operators are "and", "or", "not". Brackets can be used to create more complicated combinations.
example: R1 and not (R2 or R3)
-
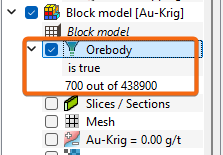
The number of filtered samples versus the total number of samples (applied rule(s) as well as the result of the filtering) is displayed as a sub-level of the filtering layer.