Material Flows
After the business areas, locations and stockpiles have been created in the Supply Chain Explorer, it is necessary to create material flows and transport routes to model the movement of materials from the mine pits to the port.
Material Flows
A material flow is also known as a 'process flow' or 'movement flow'. A material flow has a source location and a destination location, and can have a sample template to facilitate the entry of new data about the material quality. Analyte values can also be assumed; for example, if you know the quality of the material in the source stockpile.
Material flows are used when recording the movement of bulk materials or discrete units directly between two locations, when loading or unloading a despatch, when creating packages from bulk material or when unpacking packages back to bulk.
Transport routes also have a source location and a destination location but are used exclusively for despatches by rail, truck, barge or vessel.
Specific types of flows represent the flow of material through the supply chain, between locations within a business area.
Process Flows
Process flows represent the flow of bulk material to and from stock locations and despatch locations. A transaction records the flow of bulk material over a predefined process flow, either directly between stock locations, or when loading or unloading a despatch. Process flows are also required for filling and emptying transactions for bulk package groups.
Waste Process Definitions
Waste process definitions represent the flow of bulk waste material to a waste location.
Packing Process Flows
Packing process flows represent the flow of bulk material from stock locations or despatch locations to packaged material at discrete unit locations or despatch locations, or the reverse unpacking process.
Movement Flows
Discrete unit movement flows represent the movement of packaged material to and from discrete unit locations, discrete unit division and despatch locations. A movement records the flow of packaged material over a predefined movement flow, either directly between discrete unit locations, or when loading or unloading a despatch.
Quality Assumptions
The base assumption determines the quality of all analytes in the destination stockpile after a transaction or movement across the material flow has taken place, if the analyte is not specified individually on the Process Flow Analytes tab.
- No Assumptions—No assumption is made regarding quality. The destination stockpile must to be surveyed to determine quality. No quality is calculated based on the quality of the source stockpiles. This assumption is typically used on the output from a plant (for example, wash plant or concentrator). The quality of the input material does not relate to the quality of the output material. The quality is not assumed to flow through.
- Assume Source—Quality is calculated on where the material came from. To calculate this quality, MineMarket looks at the transactions that moved material onto the stockpile. These transactions came from stockpiles that had a quality. The source quality is taken, and calculated as an average, weighted over the amount of tonnage from each source stockpile.
- Assume Product—Target specification values of the movement product assigned to the transaction apply if specified. Otherwise, the target specification values of the product assigned to the stockpile are assigned to the transactions onto the stockpile. Assume Product is often used for the production of very consistent materials (for example, matte product from a smelter, or metal from a refinery). A quality result from a sample always overrules this assumed quality. In some situations, a sample is not analysed unless a client really requires it, and the product specifications are used as the final quality.
You can also specify an assumption type for each analyte that you assign to a material flow. These analyte assumptions override the base assumption for the material flow.
- Assume Null—The analytical quality is not assumed to be anything. This would only be used when a value for the analyte is determined from a sample analysis and entered manually into the system. This means that the analyte is included in one of the sample templates for the material flow, so that the sample can be created and results entered for it.
- Assume Source—Quality results are set to the same as those in the source stockpile, as returned from the State Engine at the time of transaction. A quality result from a sample always overrules this assumed quality.
- Assume Product—Quality results are set to the same as those specified on the product at the time of the transaction. The product is the movement product, if specified. If the movement product is not specified, no quality results are set.
- Assume Defaults—The quality result comes from the specified default value for this material flow. A quality result from a sample always overrules this assumed quality.
Note: Only one default value can be specified for all time. That is, if the value is subsequently changed, all non-archived transactions are downstreamed for reprocessing. An alternative approach is to use Assume Product; ensure that product specifications include the analyte target's value; and ensure that all transactions have an assigned movement product. If you later need to change the 'default' (target) value, add a new set of product specifications with a different applicable date.
- Assume Calculated—The quality result is calculated using an analyte formula. The data input to the analyte formula comes from the sample results. If no sample results are available, the calculation cannot be performed.
Important: If a calculated analyte is to be included in any weighted average calculations, it is more accurate to create an analyte definition with a Value Type of Calculated. The analyte should then not be added to the material flow because it is automatically calculated, and cannot be overridden by surveys or samples.
- Assume Retained—If a stockpile goes negative, the quality result is retained from when the stockpile had a positive quantity. If the stockpile has a positive quantity, the base assumption of the material flow applies. See Negative Stockpile Configuration.
Video
A Datamine consultant recorded this video about quality assumptions on material flows in MineMarket.
Product and Movement Product Assumptions
The product of a despatch loading or unloading transaction is the:
- Source product if only the source product is defined, or if both the source and destination products are defined.
- Destination product if only the destination product is defined.
If Auto Populate Product is checked for the material flow, the default movement product for a transaction is the:
- Source product if only the source product is defined, or if both the source and destination products are defined.
- Destination product if only the destination product is defined.
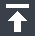
Process Flow Diagrams
A process flow diagram illustrates the locations in a business area and the material flows and transport routes between the locations. The following example is from a coal mining demo database and shows the material flows from the mining pit, through the processing plant and to the transport locations for despatch. The process flows are configured with sample templates to track quality through this supply chain.