|
|
Georeference: Two Points |
Georeferencing: Two Points
To access this function:
-
Activate the Georeference ribbon and select Two Points.
Studio Mapper presents a collection of map data objects, known as a "Map". A map can contain a variety of artefacts including a drive profile, image, contact and polygon strings, structures and so on. A map can represent a single face or a full or partial drive. This can be determined interactively as well as being predefined with Studio Mapper's System Configuration File.
Initially, a map is generated without any reference to its position in world coordinates. This "local map" is displayed using a dedicated map window that would generally be used in a 2D sense to digitize geological features and otherwise embellish the map with useful information. Studio Mapper presents this information using a dedicated "Map view". The Map view can be used both before and after georeferencing to manage the contents of a map with regards to features, comments, sketches etc.
A map is georeferenced to position it in 3D world space.
The "Two Points" method uses two defined points to orient a map along a 3D axis in world space. By default, the map is aligned vertically, but can be rotated around its axis using the Rotate tool afterwards.
As a procedure, for a non-georeferenced map:
- Display, load or create a map and display it using a map window.
- Activate the Georeference
ribbon and select Two Points,
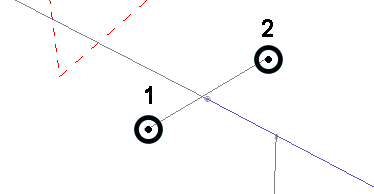
using left or right-click (snapping) e.g.:

- Activate the 3D World
window and select two points in 3D space, e.g.:
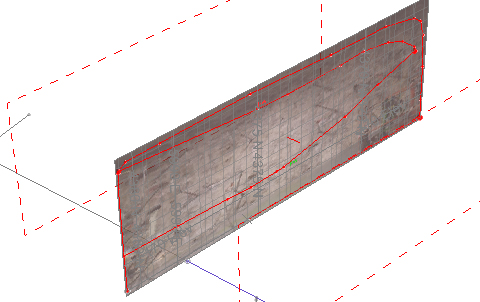
- The map is then oriented vertically, aligning point 1 on the
map and the 3D world, and orienting the azimuth of the map so
it aligns with the axis defined by point 2. Note that the map
dimensions are no affected i.e. there is no scaling performed,
e.g.:
|
|
Related Topics |
|
|
Georeferencing Methods OverviewMap and World Windows 1 Point GeolocationRefining the Map Location |
Copyright © Datamine Corporate Limited
JMN 20045_00_EN