|
|
Accessing multiple scatter plots |
Scatter Plots - Charts
To access this dialog:
-
Open the Scatter Plot dialog, select the Charts tab.
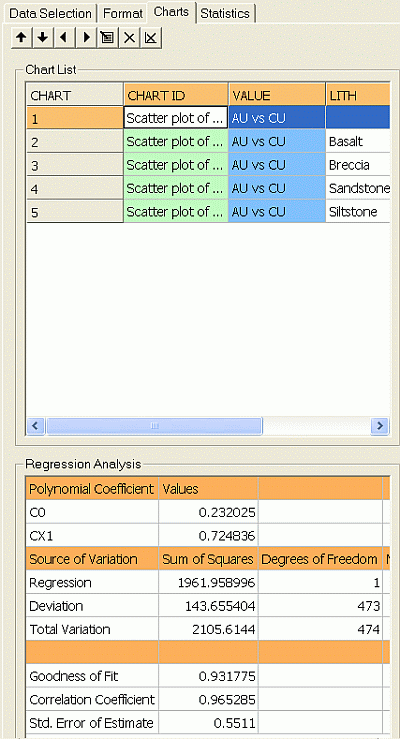
The Charts tab lists the available scatter plot charts and is used to select or delete charts, access the Chart Parameters dialog; view the Regression Analysis parameters for the selected chart.
Field Details:
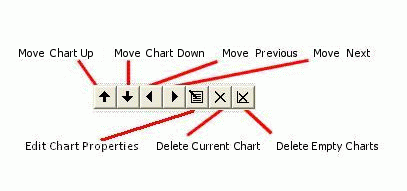
Charts Toolbar
If Multiple Charts have been created, you will have access to additional options shown along the top of the Charts panel. The Charts toolbar allows you to perform various chart-related activities on each data range.
|
|
The Charts toolbar is only available when Multiple Charts have been generated. It is not displayed for a compound chart. |
The Charts toolbar provides several functions that can be applied to each instance of a multiple chart set:
-
Move Chart Up/Down: for multiple chart entries, you can use these buttons to sort the order in which charts are listed. Selecting one of the up or down arrows will move the selected item in the corresponding direction.
-
Move to Previous/Next Chart: select (and preview) the previous/next chart in sequence.
-
Edit Chart Properties: edit the global display parameters used to display the chart that is selected, using the Scatter Plot Properties dialog.
-
Delete Current Chart: removes the current chart from the table. Note that this operation cannot be undone, but all missing charts can be replaced by regenerating them.
-
Delete Empty Charts: this button will force any charts that contain zero data to be deleted from the table.
As charts can be added to a plot sheet as a multi-page component, it is often useful to sort the charts into a sensible order. If charts are to be displayed in a table form (that is, showing several charts simultaneously), this order will also dictate the left-right and top-bottom ordering of the chart previews on the plot sheet. Find out more about chart properties...
Chart List: this group contains a table listing scatter plot charts with the following columns:
-
CHART: a simple read-only index field representing the unique numerical identifier (UID) for the chart.
-
CHART ID: a unique alphanumeric description of the chart and will be in the following format:
Scatter plot of #X Axis# vs #Y Axis#, #Key Field 1# #Key Value 1#, #Key Field 1# #Key Value 2#, #Key Field 2# ....
-
#KEY FIELD n#: a column will be displayed for each key field identified on the Data Selection tab. Each row in the Charts list will represent a unique combination of these values.
|
|
If you only wish to generate charts where key field values can be resolved, use theDelete Empty Chartsoption on theData Selectionscreen. If selected, a chart will only be generated if a value can be found for each key field that has been selected. If, for example, a drillhole data model contains ZONEs 1,2 and 3, but where the ENDDEPTH is 432 meters, all entries contain ZONE values of 1 or 2, only 2 charts will be generated for that depth. |
Regression Analysis: this group contains a table listing the regression analysis coefficients and summary statistics for the selected chart:
-
Polynomial Coefficient(s): up to 5 polynomial coefficients are listed. The polynomial equation takes the form:
Y = C0 + C1*X + C2*X2 + C3*X3 + C4*X4 + C5*X5
where the coefficients C0, C1, C2, C3, C4 and C5 are the coefficients.
-
Goodness of Fit: this equation takes the form:
Goodness of Fit = Sum of Squares / Total Variation
where:
Sum of Squares = ∑X2- [(∑X)2/N]. -
Correlation Coefficient: this is a measure of the degree of linear correlation between two variables, here the Y Axis and X Axis field values. These two variables are said to be correlated if the scatter plot shows a significant rectilinear (straight line) trend. Correlation coefficient values range from -1 (a straight line with negative slope) to 1 (a straight line with positive slope). Both ends of this range indicate strong correlation between the variables; a lack of straight line correlation is indicated by values close to zero. The formula used to calculate the correlation coefficient (cc) is as follows:
cc = (N * ∑XY - ∑X*∑Y) / sqrt((N*∑XX - ∑X*∑X) * (N*∑YY - ∑Y*∑Y))
where:
• N is the number of pairs
• ∑X is the sum of the X values
• ∑Y is the sum of the Y values
• ∑XY is the sum of the product of X and Y
• ∑XX is the sum of the product of X and X
• ∑YY is the sum of the product of Y and Y.
-
Std. Error of Estimate: this is a measure of the standard deviation of the deviations of the data around the fitted model.
|
|
These coefficients and statistics are updated when either the Polynomial Regression or the Order of Polynomial parameter is modified in the Format tab, Regression Analysis group and Apply is clicked, or these parameters are edited in the Scatter Plot Properties dialog. |
Using the Charts Tab
The number of entries that are created depends on how many distinct data series result from the selections made; for example, if multiple charts are being generated for a scatter plot where a total of 25 key field values can be found, 25 charts will be generated.
If a Compound chart is selected on the Data Selection tab, individual rows representing data series are still shown in this list. In this situation, selecting a row in the table will have no effect. However, where Multiple Charts have been generated, selecting each data row will automatically update the preview panel to show the chart that is relevant to the selection:
| |
Related Topics |
|
|
Scatter Plot Charts |