|
|
Viewing and defining Filters |
Filters

To access this dialog use one of the following:
-
In the Scheduling Setupdialog, select Constraints | Filters
-
Using the Destinations General Settings panel, Constrain by Filter group, click Filters...
The Filters dialog is used to view and define filters for use in destination grade/quality constraints.
Using Filters
Filters can be used to provide extra constraint options, in addition to material Category Constraints, to controlling which material is sent to a destination i.e. in defining Standard Constraints. The Filters panel allows you to create a set of filter expressions (or formulae) that use the variables in the Block Reserves table in conjunction with a number of standard operators.
In the example shown in the image below, filters could be used to exclude material from a particular pit being sent to a particular destination.
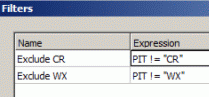
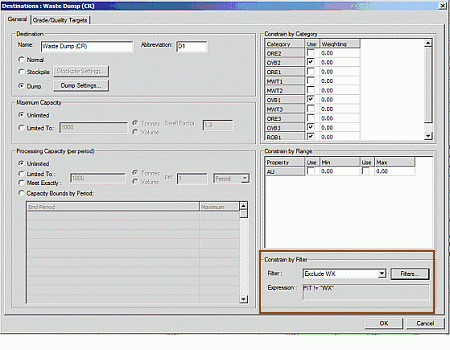
The relevant filter is then associated with a particular destination using the DestinationGeneral Settings panel (Constrain by Filter group), e.g.:


Creating a New Filter
-
In the Filters dialog, click New.
-
In the Expression Builder dialog, use the Variable Selection, Operators and Data Selection group controls to define a new filter expression, click Check Expression Validity.
-
If the expression is valid, click OK.
-
In theFiltersdialog, theFilters grid, click in theNamecell, edit the default filter name, clickOK.

Field Details:
Filters grid: select a filter for editing or copying.
Name: the filter's name.
|
|
The filter name can be edited by clicking in the cell and editing the default filter name. |
Expression: the filter expression.
New: add a new filter using the Expression Builder dialog.
Edit: edit the selected filter using the Expression Builder dialog.
Copy: create a copy of the selected filter.
Delete:
remove the selected filter from the list.
OK: click this button to save changes and close the dialog;
Cancel: click to close the dialog without saving changes.
|
| Related Topics |
| The Scheduling Data Setup DialogAbout ConstraintsGrade/Quality TargetsGlobal Mass TargetsTarget Dependencies |