Optimization Tasks
To access this control panel:
-
Display the Tasks Pane and select Optimization from the panel selection list.
The Optimization panel displays a top-bottom arrangement of schedule optimization tasks.
To navigate the workflow, either select the menu item you need, or use the navigation buttons at the top:
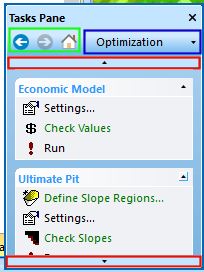
- Back, Forwards and Home: use these commands to go forward and back through your panel viewing history. This can be useful to quickly move between two regularly-used panels, for example.
- Panel Selection: use this drop-down menu to select a tasks panel (Optimization, Visualize, Reports or Notes).
- Scrollers: If the Tasks Pane is taller than the current screen resolution, use these arrows to scroll the pane contents up or down.
Tasks are only available if expected inputs are available (for example, you cannot schedule pushbacks without an economic model).
Commands are grouped into collapsible tables, each representing a key functional area of the strategic planning and optimization workflow.
Note: You can cancel processing using Abort at the bottom of the vertical menu. Once selected, processing halts at the earliest opportunity.
Optimization Control Bar Tools
The following command categories are available:
Import Data
Import data that is used in your strategic planning scenario, using the following tools:
-
Datamine Model—Only available if a model has not yet been loaded for the current case study. Import a Datamine (.dm) format model.
-
MineSight Model—Import a MineSight format model.
-
Text (CSV) Model—Import a model stored in ASCII text format, using the Text Import Wizard.
-
Other Model—Import a model using the Data Source Drivers facility. A wide range of drivers are available. See Data Import.
-
Also see Strategic Mine Planning Data.
-
Model Information—Display summary information about the currently loaded model in the Optimization Output control bar. This includes the Case Study to which the model relates, its file format, disk location and other properties.
-
Refresh Model—Refresh the loaded model and, optionally, add fields (Datamine, MineSight and CSV models only).
Note: Adding fields using the Assign Fields screen.
-
Datamine Surface—Import one or more wireframes for use in optimization. This option is used to select a Datamine wireframe triangles file.
Note: After a file and attributes have been selected for import, the Save Surface screen is used to migrate the data into the current database.
-
Other Surface—Import one or more wireframes for use in optimization. This option is used to activate Datamine's Data Source Drivers console and select a non-Datamine file (a wide range of formats are supported).
Note: After a surface file and attributes have been selected for import, the Save Surface screen is used to migrate the data into the current database.
-
Boundaries—Boundary strings representing pit limits, slope regions, pushback adjustments or pit partitions are imported using this command.
Note: Once a string and attributes have been selected, you assign the data to a particular category using the Choose Region Type screen
Economic Model
See Economic Model Essentials.
An economic model is a geological block model supporting additional information relating to the 'value' of a particular block of ore. Extend the loaded model with economic information using the following tools:
-
Settings—Define general options, commodity prices, mining costs (plus dilution and recovery), processing costs by ore type and cost adjustment factors, using the Economic Settings screen.
-
Check Values—Quickly review the current economic model settings. See Economic Model Essentials.
-
Run—Generate the economic model, based on the supplied data and parameters.
Ultimate Pit
See Pit Optimization Essentials.
Manage pit optimization settings using this group of tools, and generate the Ultimate Pit Optimal Extraction Sequence (OES):
-
Define Slope Regions—Create 3D slope regions either from 2D outlines or from 3D separating surfaces, or from a combination of outlines and separating surfaces. Displays the Make 3D Regions screen.
-
Settings—Specify how ultimate pits are generated, including annual discounting (and ore output rate), the pit calculation method, sequencing options, slope region assignment and topography (and pit limits) settings.
-
Check Slopes—Runs a slope check report. See Pit Optimization Essentials.
-
Run—Generate the ultimate pit based on your current optimization parameters for the active case study.
Pushbacks
Once the Ultimate Pit OES has been established, the pushback generation can commence. The basic objective is to create a pushback shape which meets some primary targets, namely the ore tonnage to be won from each pushback as well as its minimum mining width.
-
Settings—Define parameters for pushback generation, including global settings and distance constraints and size management.
- Run—Launch the pushback generator using the settings provided.
Scheduler
Generate the strategic schedule using the previous settings.
See Scheduler Essentials.
-
Pushback File—Schedule either Studio NPVS-generated pushbacks (default) or another pit sequence, for example, imported pushbacks. Decide which to use via the Schedule Pushbacks screen.
-
Stockpiles—Define parameters related to stockpiled material to be used when generating the schedule. Displays the Define Stockpiles for the Scheduler screen.
-
Update Economics—Use the Economic Model Settings screen to provide updated economics for the Maroma scheduler.
-
Settings—Define the settings used to schedule pushbacks, including time and truck hours, targets, search parameters and dependencies.
-
Haulage Info—Define haulage settings, including truck and ramp parameters, bench exits and review your haulage parameters.
-
Capital Costs—Define the money spent per pushback or period using the Capital Costs screen.
-
Run—Schedule your pushbacks using the settings provided. See Scheduler Essentials.
Allocation & Flow
Material Allocation Optimizer (MAO) optimizes allocation of Inputs to Destinations using Linear Programming, whereas Mine Flow Optimizer (MFO) maximizes NPV by adjusting up mining rates (cutoff grades are also optimized).
-
Update Economics—MAO and MFO can either use Economic Settings directly or can use modified economic parameters saved as a part of MAO Settings.
-
Settings—Define your general settings for material and flow optimization, including ore type rules and classes, stockpile settings, external sources and stockpiles, destinations for blended products, variables, rates and ratios and which tool to use (MAO or MFO).
-
Haulage Info—Define haulage settings for MAO, including truck parameters, destinations and destination viability. You can also export pushback exit bench data.
-
Run—Launch the Material Allocation or Mine Flow Optimizer and build the MAO-MFO model.
-
Save Model—Save the generated MAO or MFO model.
Risk Assessment
Studio NPVS and Studio Maxipit allow engineers to assess the sensitivity and resilience of mine plans to changing economic conditions that affect prices and costs. This is done using the Geological Risk Assessment command group.
See About Geological Risk Assessment (GRA).
-
Import Data—Import conditional simulation data. This is assumed to be from the same model that was used to build the economic model.
-
Make Value Model—Build equally likely value models by applying economic and recovery parameters to the grade models.
-
Evaluate OES—Evaluate probability distributions of profits and NPV of any OES.
-
Make Risk Rated Pits—Evaluate probability distributions of profits and NPV of any OES. Like any other pit, a k-Pit can be evaluated for costs, revenues, NPV, tonnages and grades.
See Geological Risk Assessment Essentials (GRA) for background information.
Related topics and activities